This article will explain what a wallet address is, how to find it in your crypto wallet, and why this product is essential in blockchain transactions. In addition, it will also outline possible risks and ways to prevent vulnerabilities.
What is a Wallet Address?
Typically referred to as a public key, a wallet address is a unique identifier used for sending and receiving digital assets across a blockchain. Think of it as your bank account number that you give to anyone who wants to send you money.
To receive a digital asset from someone, you will give them your wallet address and the corresponding network. This is like sending someone your account number and sort code.
Blockchain transactions are immutable, and the wallet address plays a crucial role. Each address is tied to a specific network, and sending it to the wrong network can result in a loss of funds.
How Do These Addresses Work?
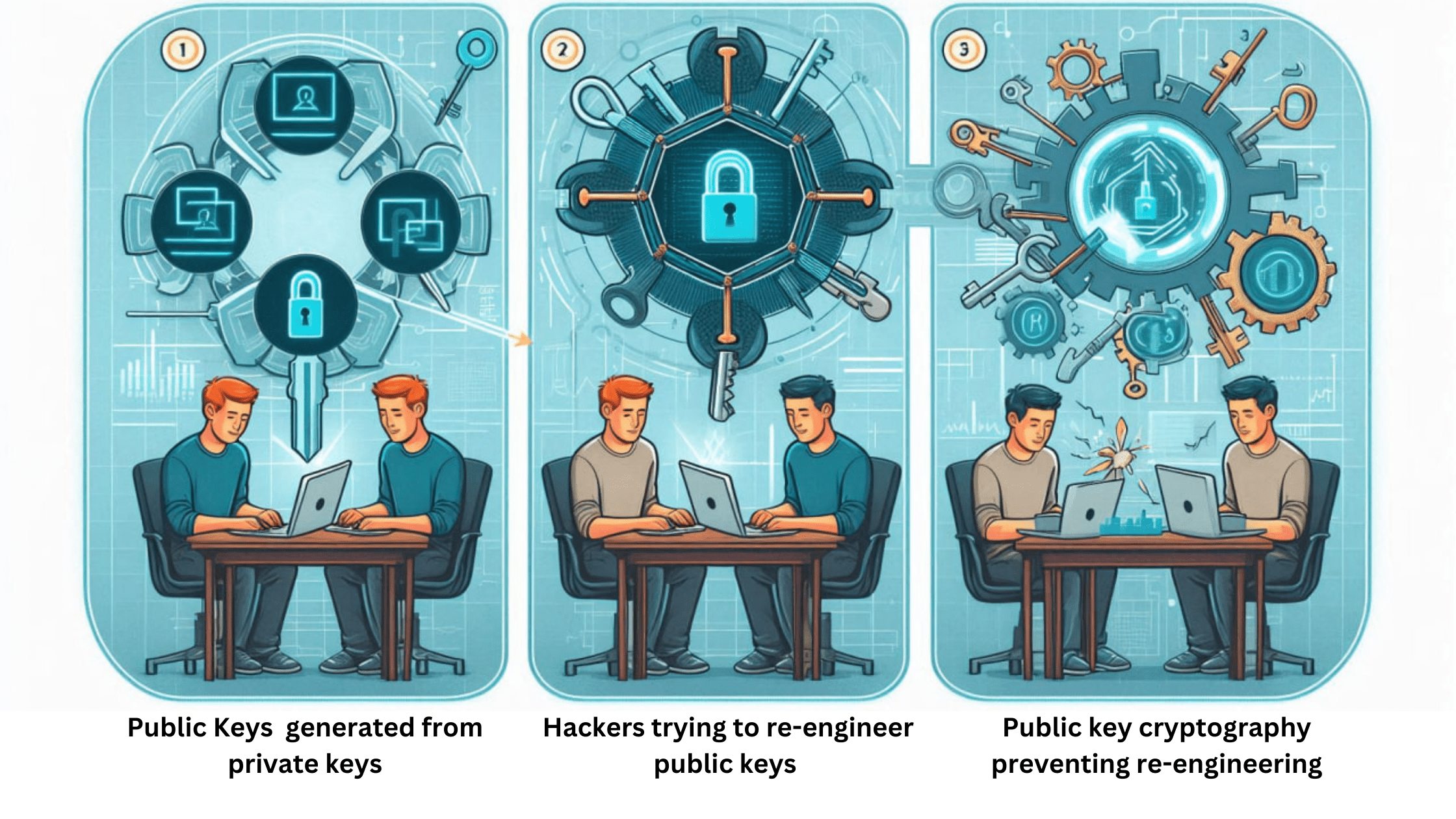
That said, how do these addresses work? As mentioned earlier, wallet addresses are typically referred to as public keys. This is because they are connected to and generated from private keys. Private keys are the equivalent of your bank account that you opened with the bank. You can get multiple account numbers to receive different currencies with that account
Similarly, the private keys are the foundation of every blockchain wallet. It is like the login details of your bank app. With your public key, an unwanted third party can access your account and steal your funds. This is why Metamask, Trust, and several other noncustodial wallets demand that people protect their private keys.
While creating the wallet address, the system employs public key cryptography. This security measure prevents hackers from reverse engineering the public keys through the private keys.
Types of Wallet Addresses
Just like the typical bank account numbers are specific to the currencies they receive, wallet addresses are usually particular to the blockchain network they use to send and receive digital assets.
Below are some of the various types of wallet addresses:
Bitcoin Wallet Addresses: Bitcoin addresses are used on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Legacy (P2PKH): Starts with “1” (e.g., 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa).
- SegWit (P2SH): Starts with “3” (e.g., 3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy).
- Bech32 (Native SegWit): Starts with “bc1” (e.g., bc1qw508d6qejxtdg4y5r3zarvary0c5xw7kygt080).
Ethereum Wallet Addresses: Ethereum addresses are used for Ether and ERC-20 tokens.
- Always starts with “0x” (e.g., 0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7).
TRON Wallet Addresses: TRON addresses are used for TRX and TRC-20 tokens.
- Typically start with “T” (e.g., TXXNg4y9HDy1WJcf3RF1Hp8z5ocf96T1cA).
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) Wallet AddressesL Used for BNB and BEP-20 tokens.
- Same format as Ethereum addresses, starting with “0x” (e.g., 0x123456789ABCDEF…).
Litecoin Wallet Addresses: Litecoin addresses are similar to Bitcoin’s but tailored to its blockchain.
- Can start with “L” or “M” (e.g., LZP7Z3xvF1B2tK2Vz6axTtBj1Kx2P78YZG).
Cardano Wallet Addresses: Used for ADA tokens.
- Longer addresses starting with “addr1” (e.g., addr1qxy2kgdygjrsqtzq2n0yrf2493p83kkfjhx0wlhf9amn8dck).
XRP Wallet Addresses (Ripple): Used for XRP transactions.
- Typically include a wallet address and a destination tag (e.g., rLkMJhSVwhatzkohcnXphnZCHT3iCFs1wt, Tag: 123456).
Polygon (MATIC) Wallet Addresses: Used for Polygon tokens.
- Same format as Ethereum addresses (e.g., 0xABCDEF123456…).
Solana Wallet Addresses: Solana addresses are unique to its blockchain.
Typically a long alphanumeric string (e.g., 5WRBQW…).
Importance of a Wallet Address
The wallet address performs two major functions. This includes those below:
- Enabling Blockchain Transactions: Without the wallet address, completing blockchain transactions will be impossible. Imagine what it would be like to send and receive money from banks without an account number.
- Ensuring User Privacy: In addition, the wallet address protects users by ensuring their privacy during transactions. Unlike regular bank accounts, nobody can ascertain your personal information by simply looking at your public key.
Tips for Using Your Wallet Address Safely
Here are some of the best practices for safely using your wallet for blockchain and crypto transactions:
- Backup Your Wallet: Ensure you can always access your wallet even when you lose your device. This is essential to protect against lost funds from stolen, misplaced, or damaged devices.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Hackers have been known to steal private information through malicious public internet connections. Only connect your devices to secure and trusted Wi-Fi to avoid falling victim.
- Use One-Time Public Addresses If Possible: Using one-time wallet addresses can help to prevent reverse engineering. It is the same as a “use once” debit card.
- Always Check The Wallet Website: Hackers have been known to clone websites of popular blockchain wallets. This tricks unsuspecting users into entering their login information, thinking it is a genuine website. Therefore, confirm the URL before logging into your account.
- Always Copy and Paste Wallet Address: Manually typing out a wallet address comprising long and complex characters is pointless. This can result in mistakes that can cause permanent funds loss. Instead, copy and paste the wallet address when sending or receiving tokens. Furthermore, confirm the network before proceeding with any transaction.
Anticipate Major SoftNote Update
Speaking of wallets and wallet addresses, Tectum is set to announce a major update to the SoftNote Wallet in the coming days. This important milestone will help spread our reach and onboard more crypto users and enthusiasts looking for a more comprehensive way to manage their tokens.
Keep your eyes glued to all Tectum social media accounts and our blog. You do not want to miss the announcement.