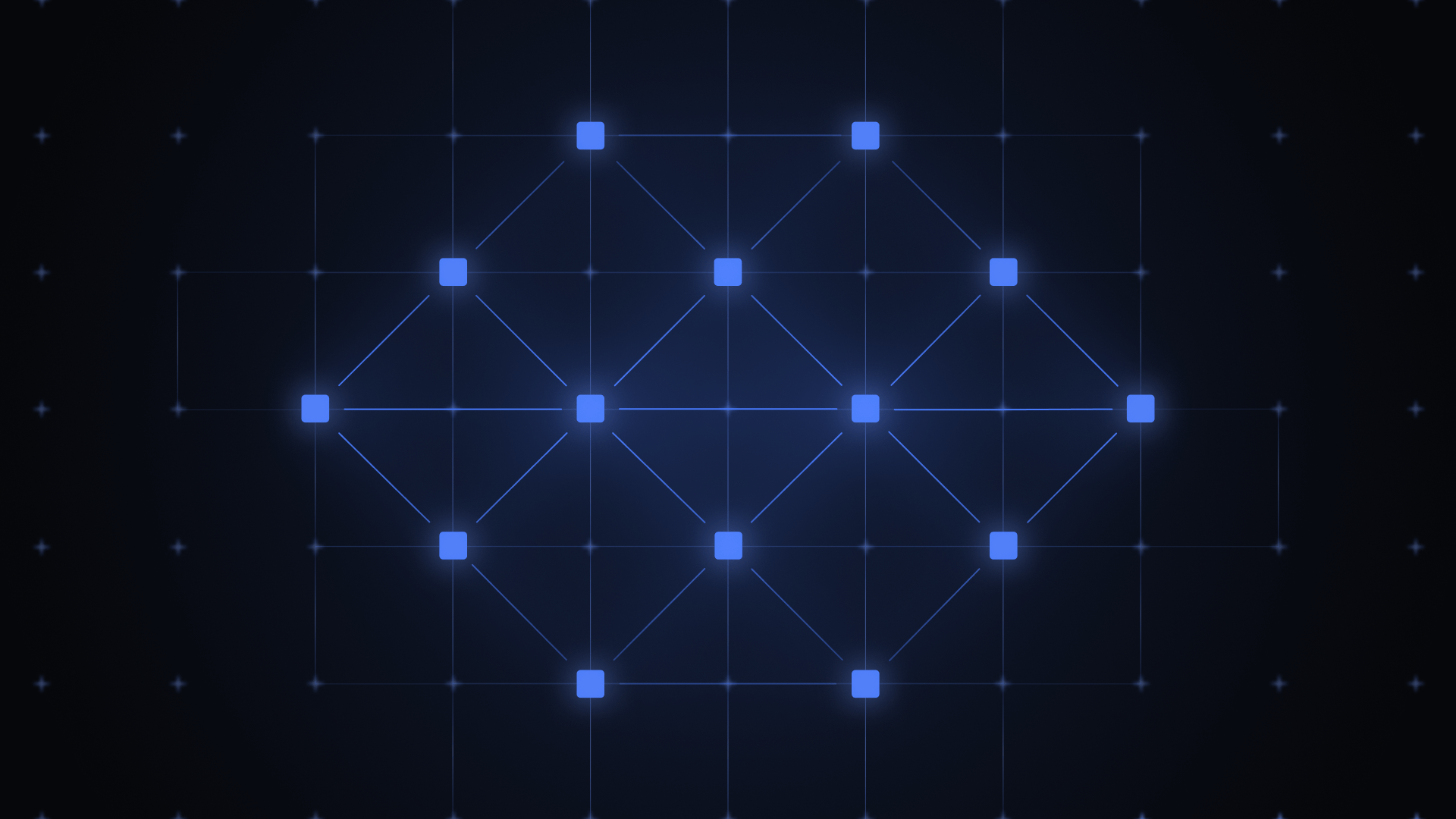
Meanwhile, most people who say this do not know what a decentralized ledger looks like. It is hard to blame them, considering there aren’t significant visualizations of decentralized technology. Perhaps this explains why
Human beings are visual learners, with more than 65% of people likely remembering what they learned if they saw images or videos. Perhaps, the lack of visual representation of decentralized ledgers explains why most people do not understand blockchain technology.
This article intends to help people overcome that barrier by showing them what blockchain looks like.
What Does Blockchain Look Like? Understanding The Basics of Decentralized Technology
Before visualizing blockchain, this article will differentiate it from orthodox technology. This will get you in tune for more technical details to come. First, how is blockchain different from centralized tech? Before talking about how blockchain is a decentralized technology that stores information in blocks that are interconnected in a chain-like structure, let’s examine how orthodox tech works.
With traditional technology, people communicate indirectly through a central server. A good example is when you are chatting with your friend or family member via an instant chatting platform like WhatsApp for example. In contrast, you are not exactly exchanging messages with each other.
What is actually happening is that you are sending the messages to a central server. Your device scrambles the message before sending it to the server. The server transmits the scrambled message to your device, which unscrambles it and you get your friend’s reply.
Meanwhile, this process happens very fast and creates the idea that you are exchanging messages directly. The problem with relying on a central server is how the system will crumble if the server is compromised. Imagine you are chatting with your friend and brother at the same time. Should anything happen to the server, you will lose communication with both your friend and your brother.
Blockchain, on the other hand, allows users to communicate through a peer-to-peer system. Instead of one central server, individual phones serve as “mini servers” that store and transfer information directly. This way, there are multiple points of failure and you can still communicate with your brother even when your friend’s phone is faulty.
What Does Blockchain Look Like: A Technical Perspective
With a clear example of differentiating blockchain from centralized technology, let’s examine what blockchain looks like. To understand what blockchain does look like, we need to look at its components separately.
Below are the major features of decentralized ledger technology:
- Blocks: These are small compartments that store information about each chat with either your brother or friend. With more messages sent, more blocks will be added to the chain to update existing information.
- Nodes: Consider Nodes to be the gatekeepers of every blockchain to ensure security and standardization. They properly screen every block before they are added to the chain.
- Consensus Mechanism: Also considered as the network protocol, this is the process that determines how the blockchain will store your chats. Will the messages be saved after every 10 chat sessions or every 10 minutes? The consensus mechanism determines this process in blockchain tech.
- Cryptographic Hash: Ever heard the term, “blockchain is immutable/permanent”? The cryptographic hash function is what enables this permanency. As a new block is added to the chain, the cryptographic hash attaches the details of the new block and those of the previous block. Besides immutability, this function also maintains the history of transactions in a blockchain.
- Decentralized Ledger: The decentralized ledger is the foundation of every blockchain technology. It is where new blocks are added and holds details of previous blocks. Think of it like the folder holding all previous backups of WhatsApp chats.
- Public and Private Keys: Recall the example of how your device scrambles the chat before sending it to your friend’s phone that unscrambles the message. Replace the phones in this case with private and public keys. The private key scrambles the sender’s message and sends it to the receiver’s public key, which unscrambles it.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain Visualization
We’re almost going crazy with all the hypothetical examples and imaginary scenarios. However, blockchain is not just some abstract phenomenon. In fact, there are already existing applications of blockchain today to give you some perspective about the technology.
Here are some use cases to help you visualize decentralized tech at work:
- Finance: Block explorers can help people view transactions as they occur in real-time. You get to see how cryptocurrency and NFT transfers happen, and how blocks are added to the chain.
- Supply Chain: In supply chain management, companies can see the location of transiting goods or vehicles in real-time on dedicated software programs and hardware devices. These technologies also permanently store all information, to prevent anyone from changing the details. This measure prevents fraud or anyone from tampering with logistical information.
- Healthcare: Instead of paper files, blockchain technology can actually help doctors access patient information on the chain. All they simply need to do is use the patient’s name to search for their information. They can also send the patient’s information to another doctor in the event of a referral to another hospital.
- Asset Management: In asset management, people tokenize real-life assets on a blockchain. This enables them to easily access and transfer these properties regardless of their location. Instead of waiting to physically meet a buyer, you can send them a tokenized document of your house and car to sign. Once the document is signed on-chain, the records are permanently stored.
Tools and Platforms for Visualizing Blockchain

For deeper analysis, data visualization software helps map blockchain activity in a way that highlights patterns and trends. These tools transform raw blockchain data into visually engaging representations:
- Tableau: This tool is popular for its powerful analytics. Tableau is preferred by blockchain experts, with its custom dashboards that display blockchain metrics such as transaction volume, gas fees, and network growth over time.
- Power BI: Another robust business intelligence tool, Power BI enables users to connect to blockchain APIs and generate interactive reports and visualizations.
- Dune Analytics: Specifically tailored for blockchain enthusiasts, Dune Analytics allows users to query blockchain data and build customizable charts and dashboards without needing extensive coding skills.
Besides technical tools, there are specialized platforms that make it easier for beginners to understand what blockchain looks like. These often include tutorials, sandbox environments, and gamified learning modules that enable people to learn without any risk or unnecessary exposure:
- Remix IDE: An online development environment for creating and testing smart contracts on Ethereum. It enables beginners to experiment with Solidity code and deploy contracts in a simulated blockchain environment.
- Alchemy University: This platform provides educational resources and interactive labs where users can learn about blockchain fundamentals and practice building decentralized applications (dApps).
- CryptoZombies: Unlike other blockchain visualizing tools, this game-based platform teaches users how to code smart contracts. The process involves individuals following simple guidelines to create their own zombie-themed blockchain game.
Challenges in Visualizing Blockchain Technology
While there is significant progress in visualizing blockchain, several challenges still hinder widespread its understanding and adoption. These challenges include the following:
- Complexity of Blockchain Concepts: Blockchain involves intricate processes such as consensus mechanisms, cryptographic hashing, and decentralized ledgers. Current visualization methods often struggle to simplify these complex ideas without oversimplifying them to the point of inaccuracy. For instance, diagrams showing blocks linked together in a chain may fail to convey the underlying security mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake algorithms. This gap leaves users with an incomplete understanding of how blockchain operates.
- Scalability of Data Representation: As blockchains grow in size and complexity, visualizing large datasets becomes increasingly challenging. A single blockchain network can process thousands—or even millions—of transactions daily, making it difficult to represent all this activity in a meaningful way. Traditional charts and graphs risk becoming cluttered and overwhelming, especially for non-technical audiences. Tools must evolve to handle scalability while maintaining clarity and usability.
- Interpretability of Visuals: Oversimplified diagrams or misleading infographics can perpetuate misconceptions about blockchain. For example, some visuals portray blockchain as merely a database or a secure ledger, neglecting its transformative potential in areas like decentralization and trustless systems. Such oversights undermine the true value proposition of blockchain technology. Ensuring that visualizations are both accurate and accessible is essential for fostering genuine comprehension.
The Role of Art and Design in Blockchain Visualization
Art and design are increasingly recognized as powerful tools for making blockchain technology more accessible, engaging, and understandable. By combining aesthetics with functionality, artists and designers are creating innovative ways to visualize what does blockchain look like, helping bridge the gap between technical complexity and user comprehension.
Here are some vital roles art and design can play in blockchain visualization:
- Blockchain-Inspired Art: Artists are leveraging blockchain as a subject and medium to create works that bring abstract concepts to life. Through paintings, digital art, and installations, they make decentralized systems tangible and relatable.
- Animations and Visual Storytelling: Animations provide a dynamic way to explain blockchain mechanics through storytelling, breaking down processes like mining, hashing, and smart contract execution into visually appealing sequences.
What Does Tectum 4.0 Blockchain Look Like?
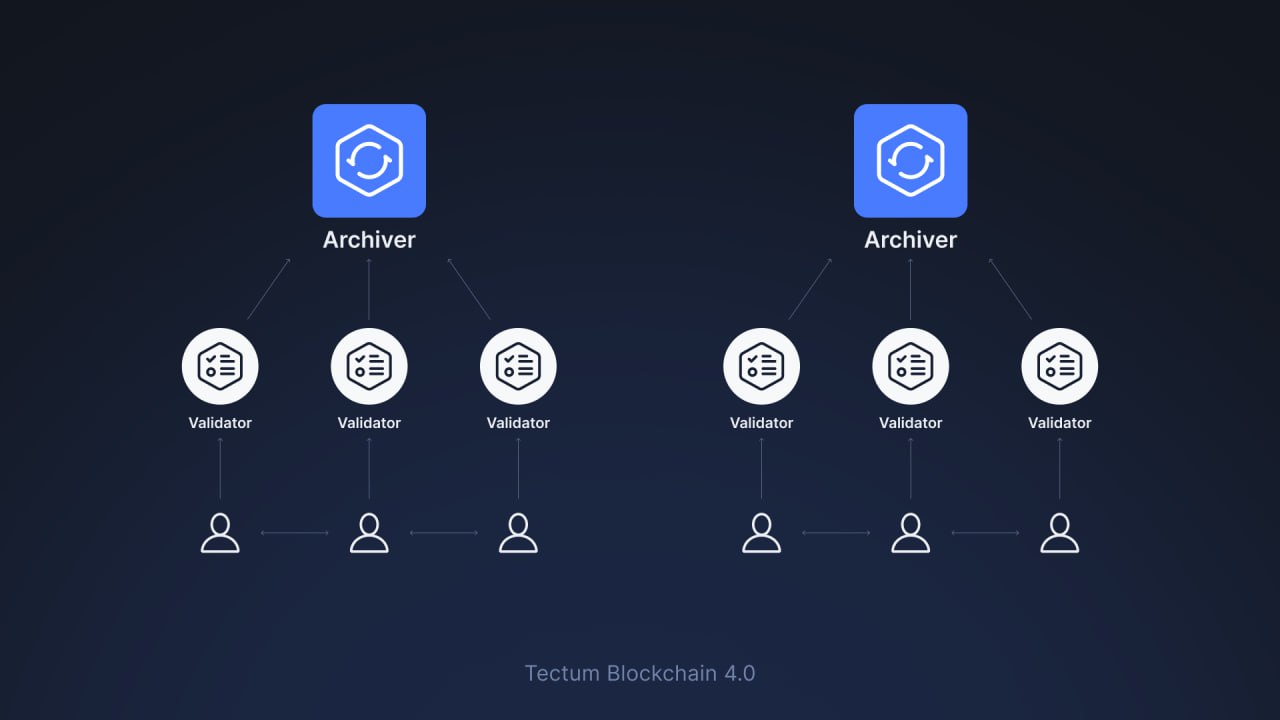
Not too long ago, we launched the Tectum 4.0 blockchain, which will function independently and be more decentralized from Tectum 3.0. Considering this article is about visualizing blockchain technology and helping people understand how it works, there is no better way to understand the 4.0 version of our network.
Therefore, what does the Tectum 4.0 blockchain look like? For better insight, you have to refer to the article “Understanding the Tectum 4.0 mainnet architecture”.
Tectum 4.0 has the following main components:
- Node Validator: Receives and validates transactions from the Node Archiver. Earns commissions depending on the number of transactions it processes.
- Node Archiver: Distributes transactions to nodes according to preset principles, before receiving and sending the validated transactions to the key Archiver.
- Key Archiver: The Key Archiver
For emphasis, below is an explanation of how Tectum 4.0 architecture operates:
The Node Archiver receives transaction requests, which it sends to the Validators. Upon receiving these transactions, Node validators authenticate them before sending the validated transactions back to the Node Archiver.
The Node Archiver conducts final checks before sending the validated transactions to the Key Archiver. In turn, the Key Archiver adds the transactions to the blockchain as a new block, making the transfer permanent and immutable.
Meanwhile, it is very easy to become a Node Validator and earn commission on the transactions you validate. Simply install the Tectum Node on your computer and stake TET. Even better, there are no lower limits as to how much you can lock. Users can stake as little as 1 Tectum Emission Token.